BusinessAnalyst

BUSINESS ANALYST
Explore The World of Business Analyst.
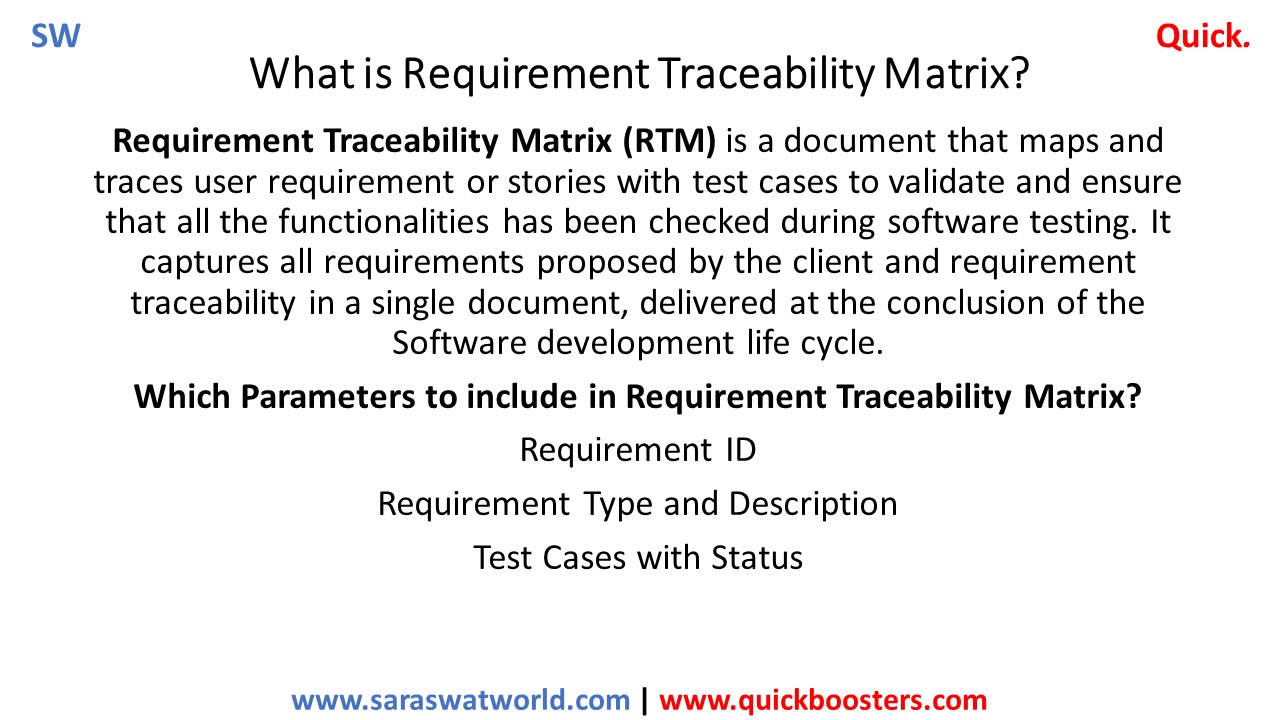
What is Requirement Traceability Matrix?
Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a document that maps and traces user requirement or stories with test cases to validate and ensure that all the functionalities has been checked during software testing. It captures all requirements proposed by the client and requirement traceability in a single document, delivered at the conclusion of the Software development…

What are Acceptance Criteria and Acceptance Test?
What are Acceptance Criteria? Acceptance criteria are a set of conditions that software must meet in order to be accepted by a customer or stakeholder. And how are these conditions decided?It’s all up to the product owner. They need to determine whether the feature is doing what the users want it to do (user story).…

What is Velocity?
What is velocity? Velocity is a unit of measurement that determines the amount of work, team can handle during an iteration. How velocity is measured? It’s measured by calculating the average number of tasks/user stories completed in a sprint. Agile teams use a velocity chart to do this.

What are Epic, Story and Initiatives?
What is Epic? An epic is a big idea or feature or business requirement that can be broken down into smaller user stories with unified goal. What is story? Story also known as user story, it is short requirement or request written from the perspective of an end user. A story is one simple narrative;…

What are the Five Values of Scrum?
Scrum’s five core values support the pillars. They are the following: Commitment. The team is self-directed, and everyone is dedicated to doing the work that has been agreed upon. Courage. The team operates as one entity and succeeds or fails together. Members do the right thing and take on tough problems. Focus. Distractions are limited,…
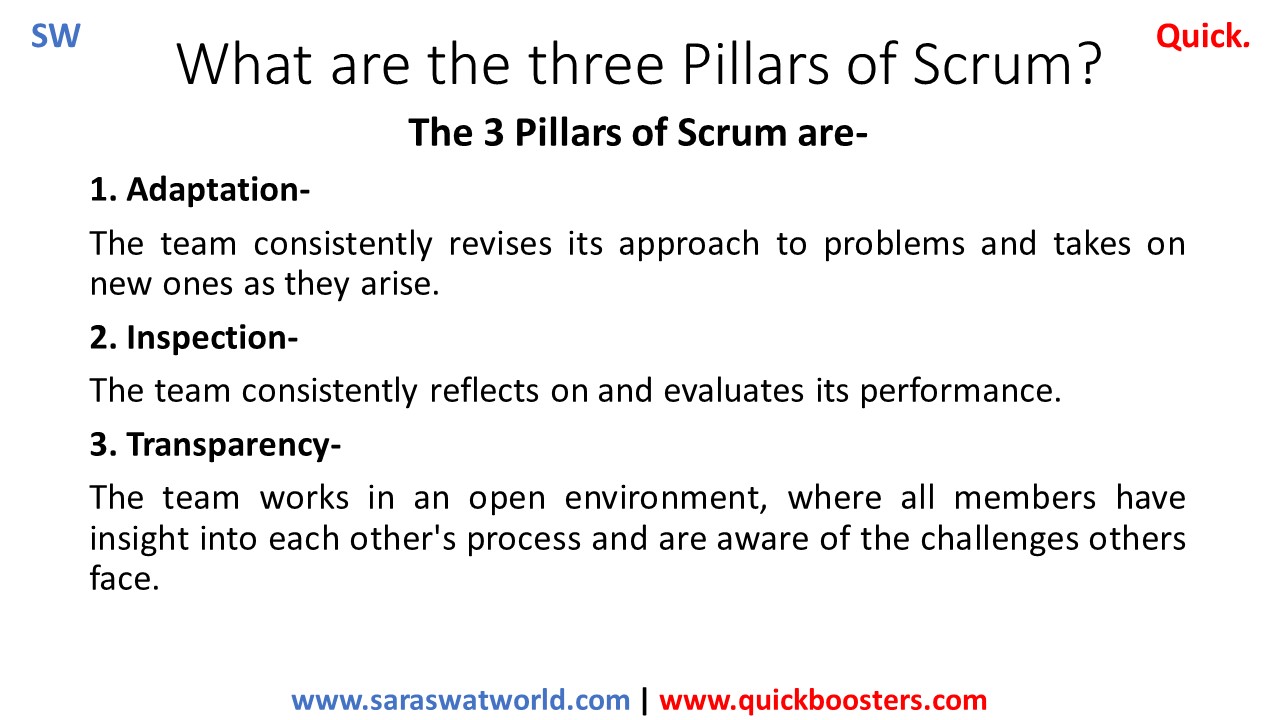
What are the three Pillars of Scrum?
The three pillars of Scrum Adaptation. The team consistently revises its approach to problems and takes on new ones as they arise. Inspection. The team consistently reflects on and evaluates its performance. Transparency. The team works in an open environment, where all members have insight into each other’s process and are aware of the challenges…

What are Scrum Artifacts?
Scrum Artifacts Product itself- The Scrum model expects the team to bring the product or system to a potentially shippable state at the end of each Scrum sprint. Product Backlog- This is the complete list of the functionality that remains to be added to the product. The product owner prioritizes the backlog so the team…

What is Scrum?
What is Scrum? Scrum is adaptable, fast, flexible and effective agile framework or agile development methodology of rules, roles, events, and artifacts used to implement Agile projects based on an iterative and incremental approach and processes to deliver value to the customer throughout the development of the project. Scrum Process Scrum relies on a self-organizing,…

What are the 12 principles of Agile?
Agile project management was established on four values and twelve principles. These values and principles are rooted in the Agile Manifesto, which was created in 2001 by seventeen managers of software development. 12 Principles are based on Agile Manifesto- Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.…
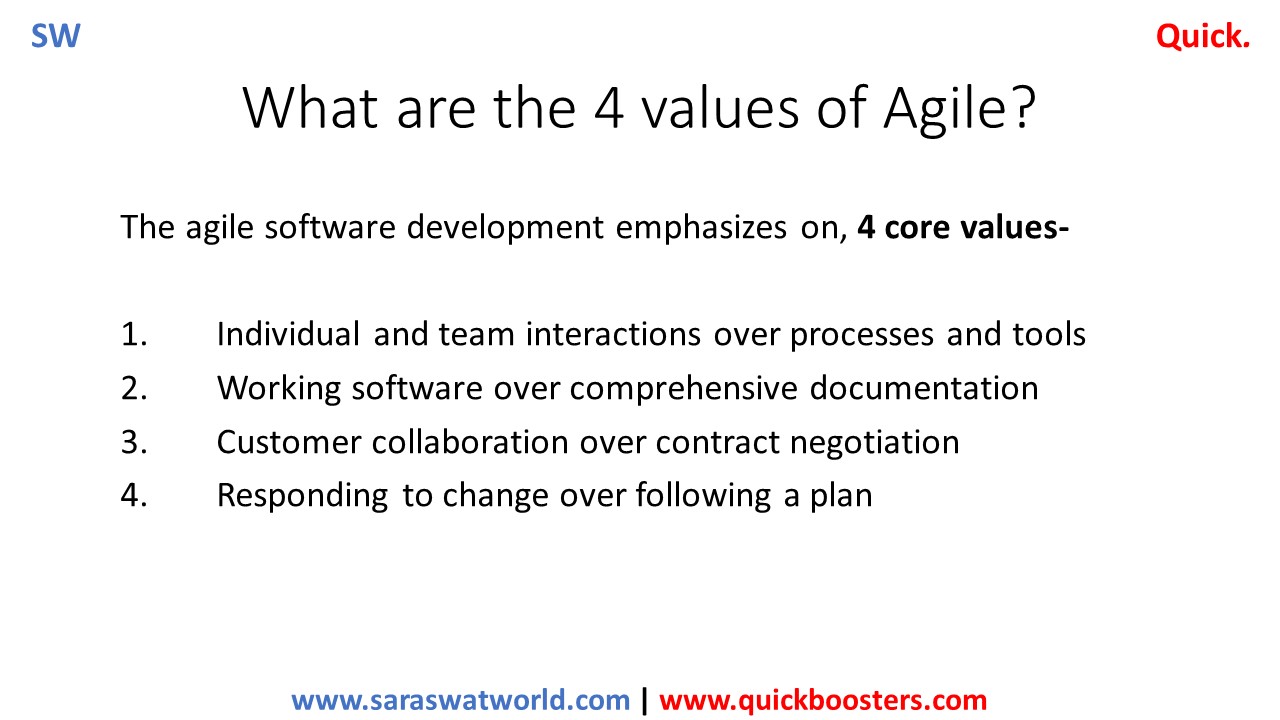
What are Four Values of Agile?
Agile values and principles Agile project management was established on four values and twelve principles. These values and principles are rooted in the Agile Manifesto, which was created in 2001 by seventeen managers of software development. The agile software development emphasizes on following 4 core values of Agile- Individual and team interactions over processes and…

What is Agile?
Agile is an approach to project management with incremental and iterative steps to completing projects. The Agile prioritizes quick delivery, adapting to change, and collaboration rather than top-down management and following a set plan. Agile is a process that allows a team to more efficiently manage a project by breaking it down into several stages,…

What is Use case?
A use case is a diagrammatic description of a system that describes how a user interacts with it to achieve a goal. It is an important aspect of software engineering and software modelling since it specifies the desired functionalities as well as the resolution of any potential faults that a user may face. A use…
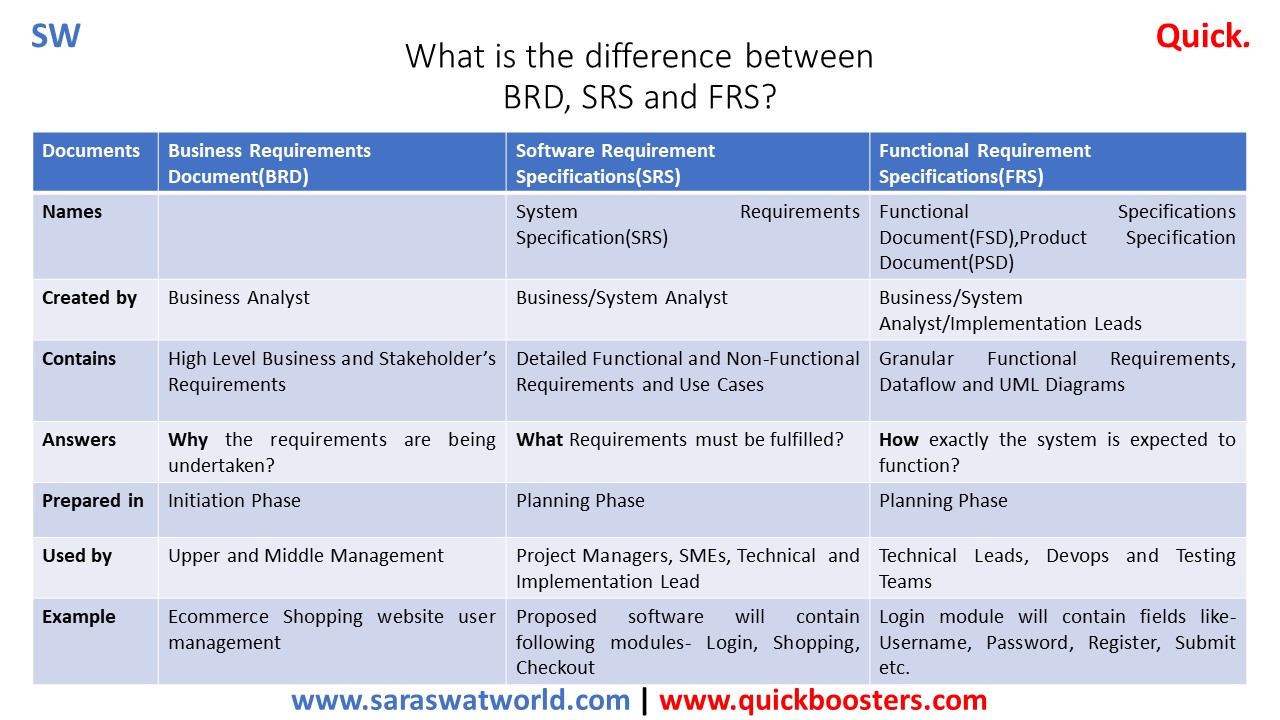
What is the difference between BRD, SRS and FRS?
Difference between BRD, SRS and FRS. BRD VS SRS VS FRS

What is FRS?
What is FRS

What is SRD or SRS?
A Software Requirement Specifications (SRS) document is a detailed and structured requirements document that contains the functional requirements (illustrates behaviour), non-functional requirements (depicts characteristics) along with any use cases that the software must fulfil. SRS states ‘What’ requirements must be fulfilled to satisfy the business’s needs and in accordance to it elaborates BRD’s high-level statements…
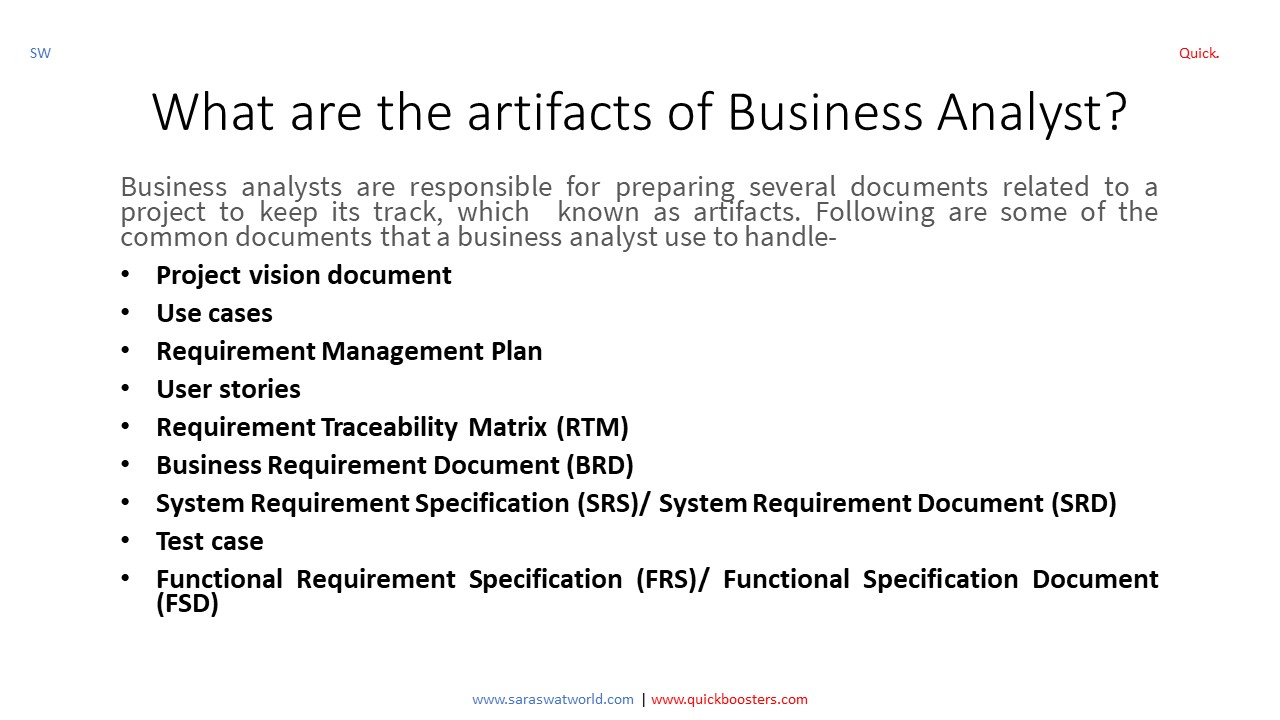
What are the Artifacts of Business Analyst?
Artifacts of Business Analyst