Saraswat World

HOW TO USE WHERE CLAUSE IN SQL?
WHERE WHERE clause in SQL is a data manipulation language (DML) statement. WHERE clause is used in filter the records based on satisfying specific condition(s). Syntax- SELECT column_name1, column_name2, …column_nameN FROM <table_name> WHERE <condition>; Example- SELECT CustomerName FROM Customers WHERE Country=‘Germany’; Description- The records having values from column_name1, column_name2, …column_nameN will be filtered and retrieved from table_name on meeting the condition provided…
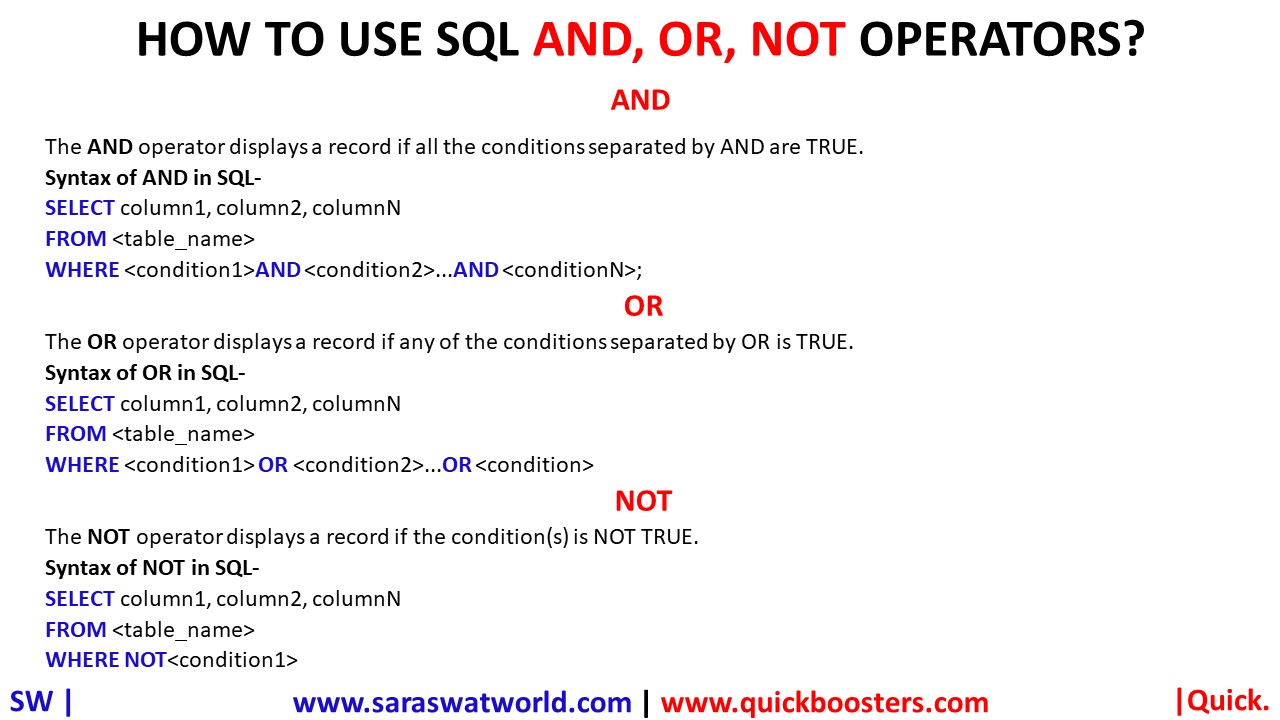
HOW TO USE SQL AND, OR, NOT OPERATORS?
AND OPERATOR IN SQL The AND operator displays a record if all the conditions separated by AND are TRUE. Syntax- SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM <table_name> WHERE <condition1>AND <condition2>…AND <conditionN>; OR OPERATOR IN SQL The OR operator displays a record if any of the conditions separated by OR is TRUE. Syntax- SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM…

HOW TO USE SQL ORDER BY CLAUSE?
ORDER BY CLAUSE ORDER BY keyword sorts the records in ascending order by default. To sort the records in descending order, use the DESC keyword. Syntax to sort the records in ascending order: SELECT ColumnName1,…,ColumnNameN FROM <TableName> ORDER BY <ColumnName> ASC; Syntax to sort the records in descending order: SELECT ColumnName1,…,ColumnNameN FROM <TableName> ORDER BY <ColumnName>DESC; Syntax to sort the records in ascending order without…
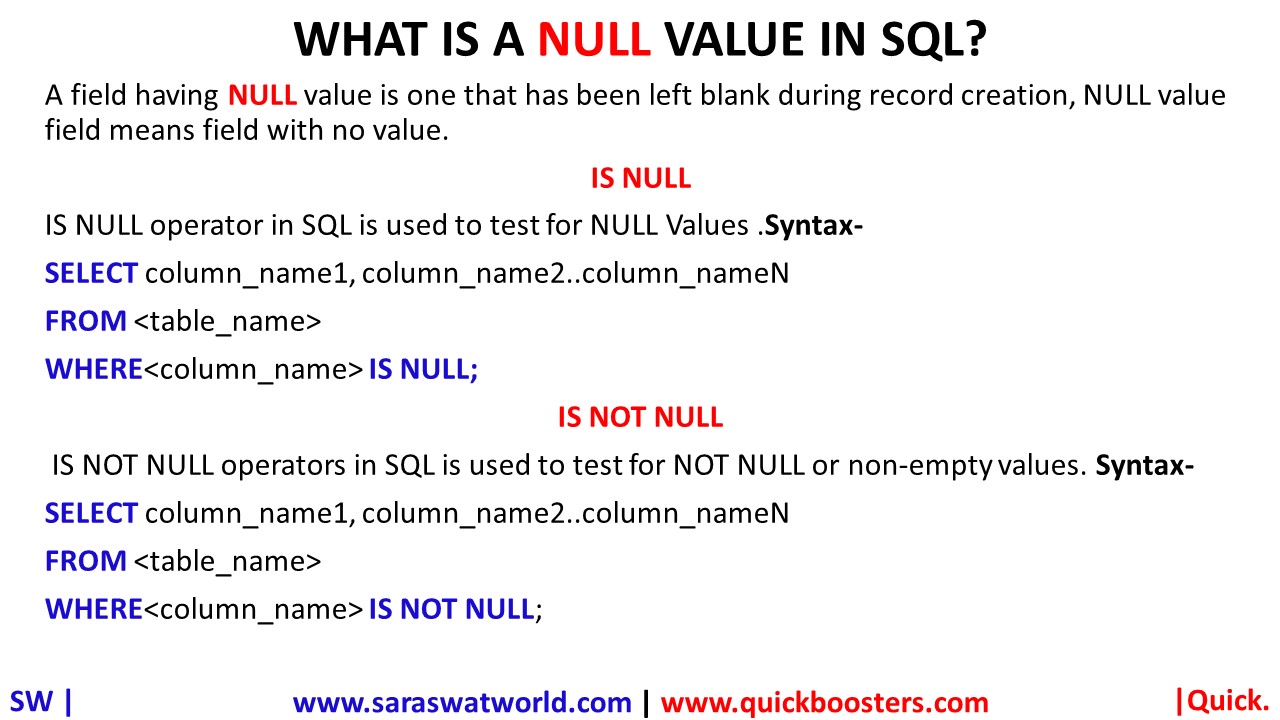
WHAT IS A NULL VALUE IN SQL?
A field having NULL value is one that has been left blank during record creation, NULL value field means field with no value. IS NULL IS NULL operator in SQL is used to test for NULL Values . Syntax- SELECT column_name1, column_name2..column_nameN FROM <table_name> WHERE<column_name> IS NULL; IS NOT NULL IS NOT NULL operators in SQL is used to test…

HOW TO USE SELECT TOP CLAUSE IN SQL?
SELECT TOP SELECT TOP clause is used to specify the number of records to return from top of the table. Syntax of TOP clause in SQL server – SELECT TOP number|PERCENT ColumnName1,…,ColumnNameN FROM <TableName> WHERE<condition> ; Example of TOP clause in SQL server –– To select top 10 records of customers from city Berlin from customers table SELECT TOP 10 * FROM Customers WHERE city=‘Berlin’; Example- To…
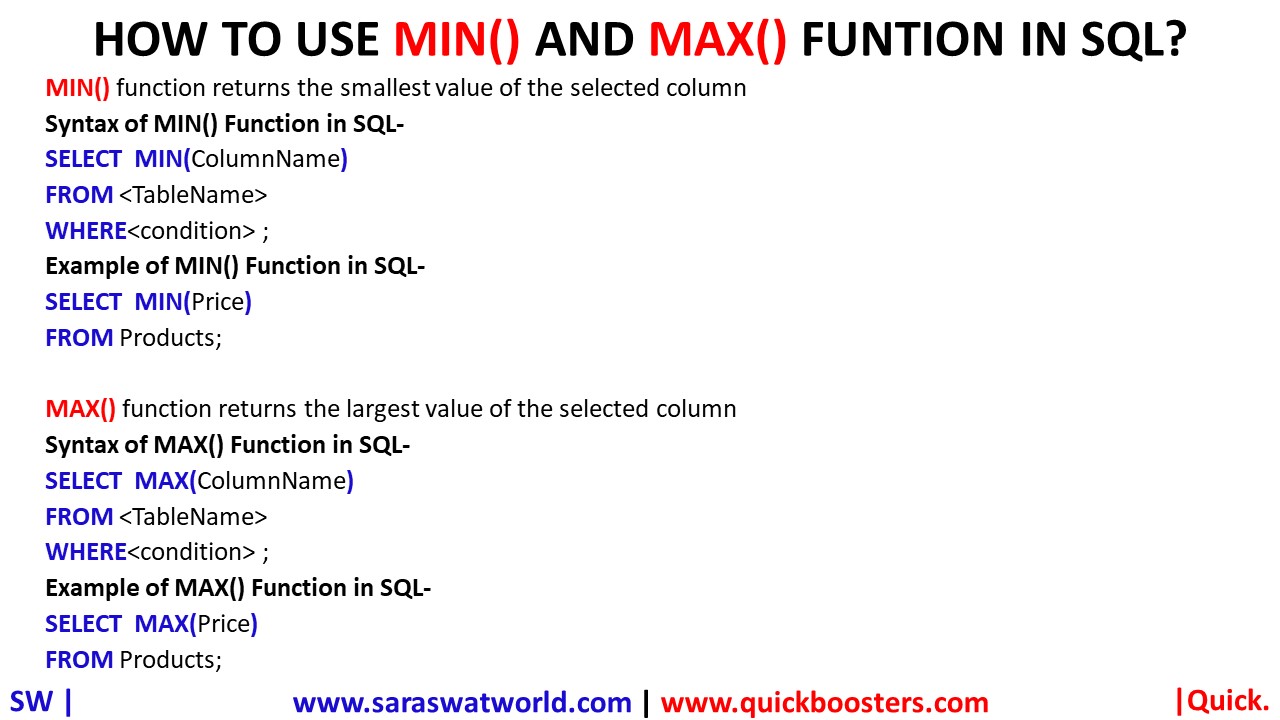
HOW TO USE MIN() AND MAX() FUNTION IN SQL?
MIN() AND MAX() MIN() function returns the smallest value of the selected column Syntax – SELECT MIN(ColumnName) FROM <TableName> WHERE<condition> ; Example- SELECT MIN(Price) FROM Products; MAX() function returns the largest value of the selected column Syntax – SELECT MAX(ColumnName) FROM <TableName> WHERE<condition> ; Example- SELECT MAX(Price) FROM Products; Note- Northwind database is used for examples.
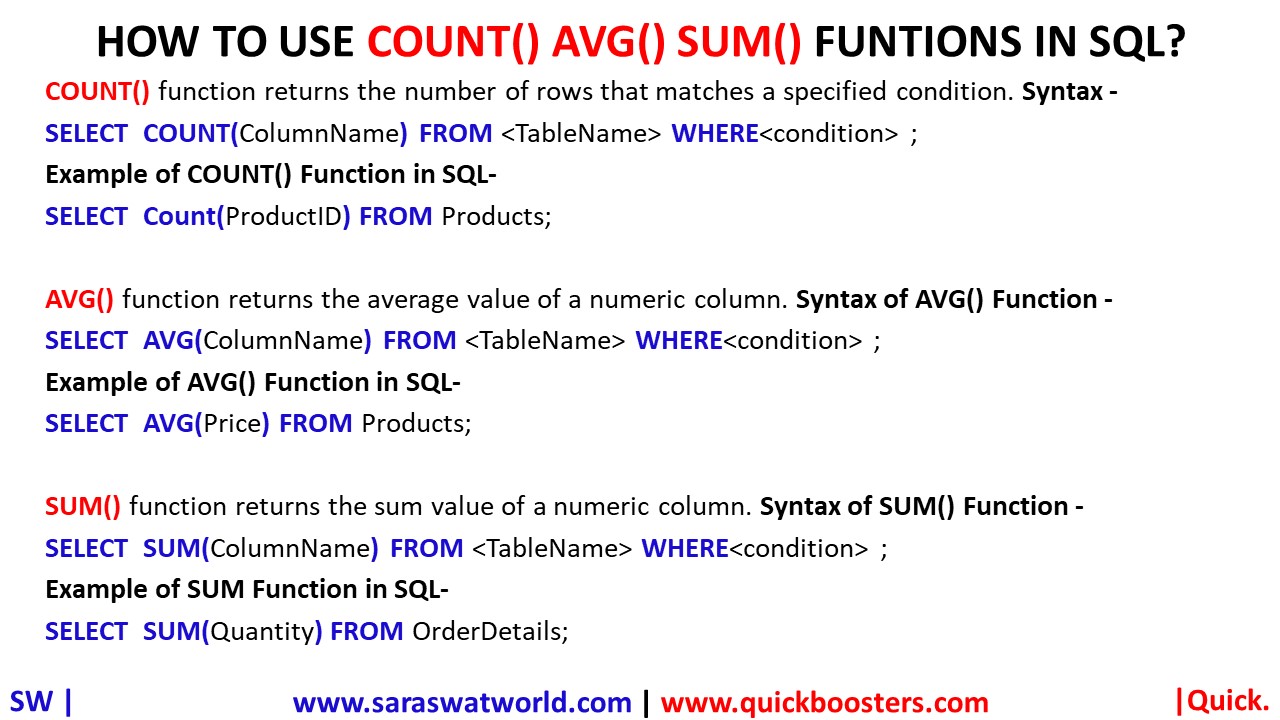
HOW TO USE COUNT() AVG() SUM() FUNTIONS IN SQL?
COUNT() function returns the number of rows that matches a specified condition. Syntax – SELECT COUNT(ColumnName) FROM <TableName> WHERE<condition> ; Example- SELECT Count(ProductID) FROM Products; AVG() function returns the average value of a numeric column. Syntax – SELECT AVG(ColumnName) FROM <TableName> WHERE<condition> ; Example- SELECT AVG(Price) FROM Products; SUM() function returns the sum value of a numeric column. Syntax – SELECT SUM(ColumnName)…

HOW TO USE LIKE OPERATOR IN SQL?
LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column. SQL LIKE Operator uses following two wildcard characters in conjuction or independently- 1.% (Percent Sign)- It matches zero, one or more than one characters. 2._ (Underscore Sign)– It matches only one or a single character. Syntax – SELECT(ColumnName(s)) FROM <TableName> WHERE<ColumnName>LIKE <pattern> ; Examples-…

HOW TO USE WILDCARD CHARACTERS IN SQL?
WILDCARD characters are used to substitute one or more characters in a string and used with LIKE operator which is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column. Syntax in SQL to use Wildcard characters – SELECT(ColumnName(s)) FROM <TableName> WHERE<ColumnName>LIKE <pattern> ; Examples of wildcard characters use in SQL- Replace the word pattern provided…

HOW TO USE IN OPERATOR IN SQL?
IN operator is used to reduce use of multiple OR conditions by specifying multiple values in WHERE clause. Syntax of IN operator in SQL – SELECT(ColumnName(s)) FROM <TableName> WHERE<ColumnName> IN (value1, value2…valueN) ; Example of IN operator in SQL- SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City IN (‘Berlin’,’London’,’Madrid’); –It will select all the customers from any of the cities Berlin, London and…

HOW TO USE BETWEEN OPERATOR IN SQL?
BETWEEN operator fetches the records from the table within the range specified in the query. Between Operator includes the starting and ending values of the specified range. Syntax of BETWEEN in SQL- SELECT(ColumnName(s)) FROM <TableName> WHERE<ColumnName> BETWEEN value1 AND value2; Example of BETWEEN in SQL- SELECT * FROM Products WHERE Price BETWEEN 18 AND 22; –It will select all the products with a price between…
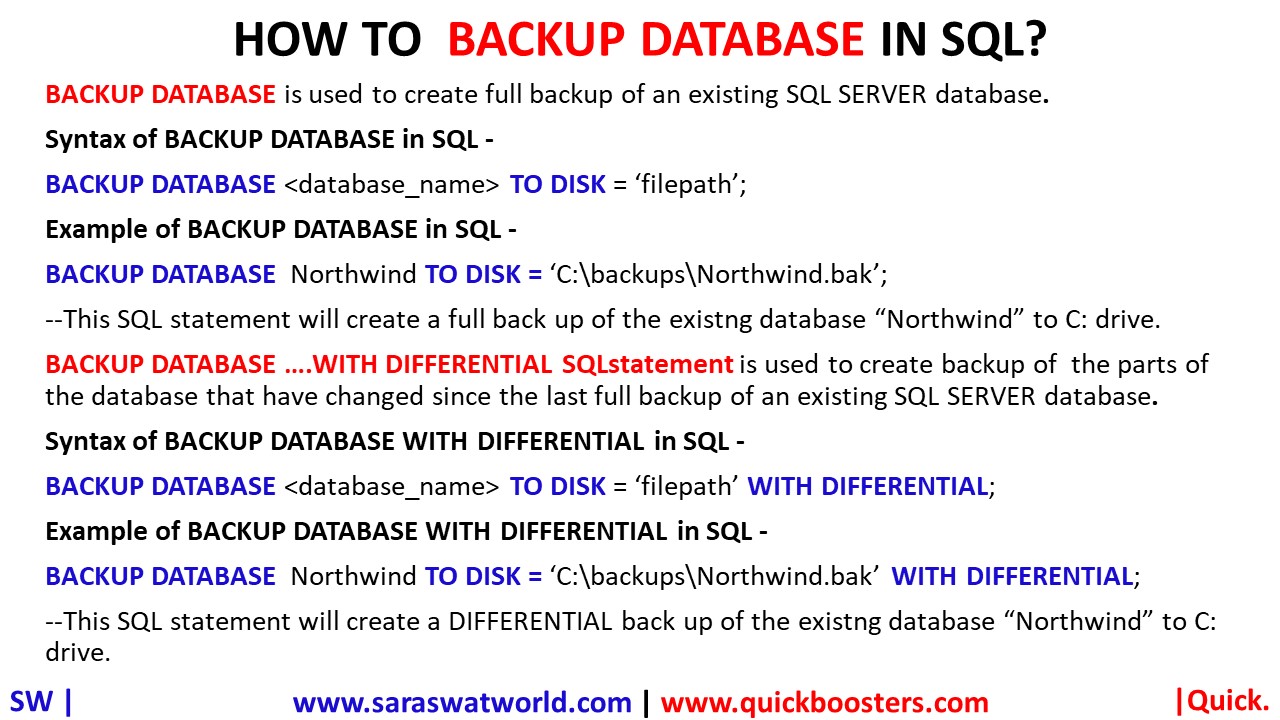
HOW TO BACKUP DATABASE IN SQL?
BACKUP DATABASE is used to create full backup of an existing SQL SERVER database. Syntax of BACKUP DATABASE in SQL – BACKUP DATABASE <database_name> TO DISK = ‘filepath’; Example of BACKUP DATABASE in SQL- BACKUP DATABASE Northwind TO DISK = ‘C:\backups\Northwind.bak’; –This SQL statement will create a full back up of the existng database “Northwind” to C: drive. BACKUP DATABASE…
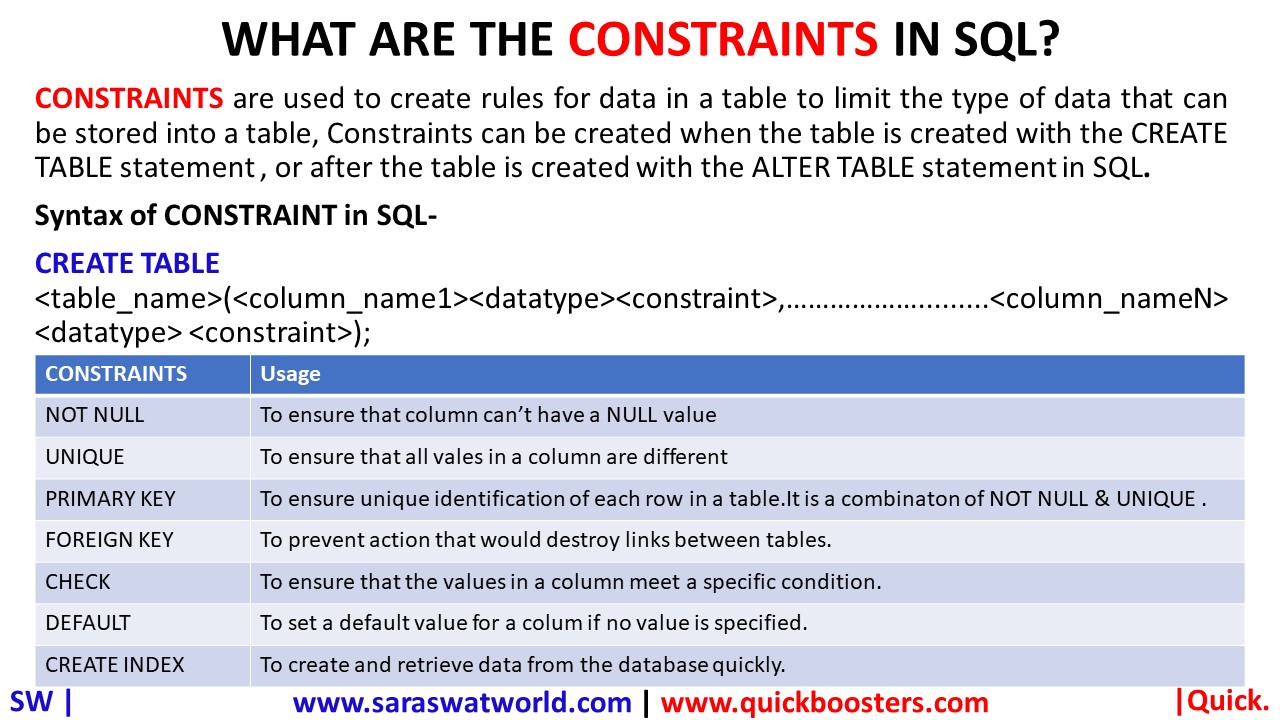
WHAT ARE THE CONSTRAINTS IN SQL?
CONSTRAINTS are used to create rules for data in a table to limit the type of data that can be stored into a table, Constraints can be created when the table is created with the CREATE TABLE statement , or after the table is created with the ALTER TABLE statement in SQL. Syntax of CONSTRAINTS in…
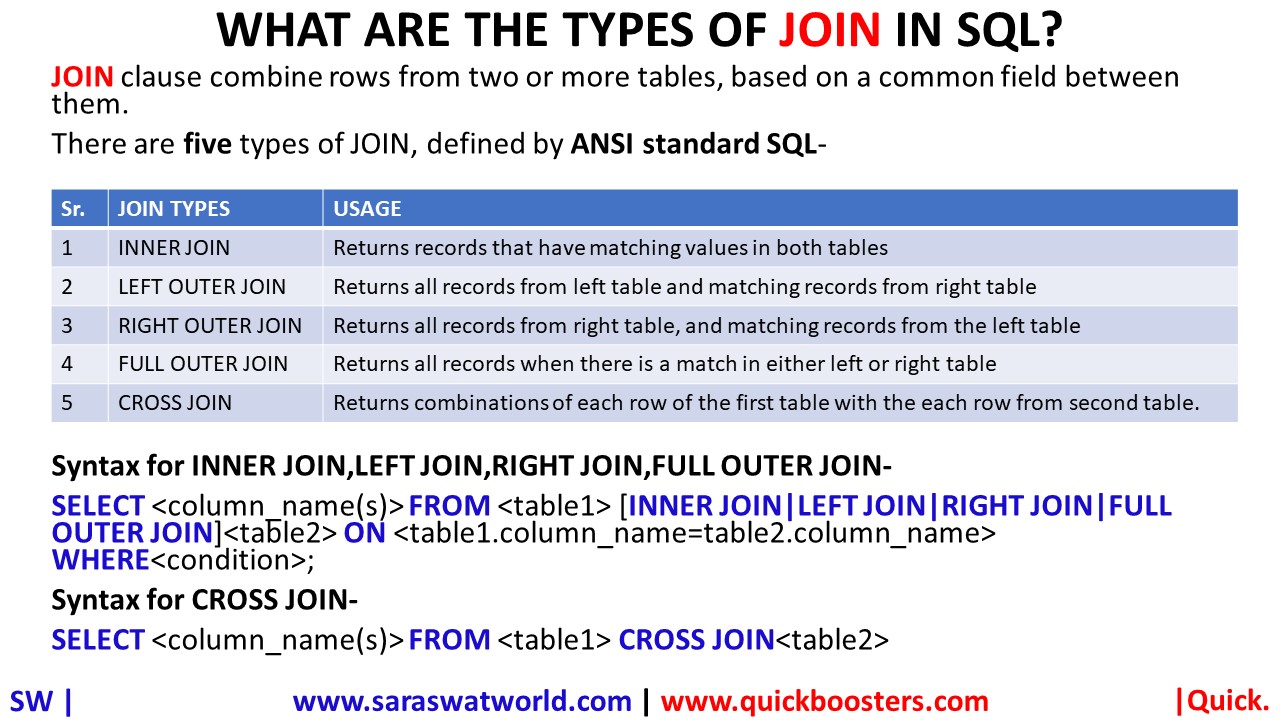
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF JOINS IN SQL?
JOIN clause combine rows from two or more tables, based on a common field between them. There are five types of JOIN, defined by ANSI standard SQL– Sr. JOIN TYPES USAGE 1 INNER JOIN Returns records that have matching values in both tables 2 LEFT OUTER JOIN Returns all records from left table and matching records from right table…

HOW TO USE INNER JOIN IN SQL?
INNER JOIN clause select all the records from both the tables when there are the values matching between the specified columns. Syntax of INNER JOIN in SQL- SELECT <column_name(s)> FROM <table1> INNER JOIN<table2> ON <table1.column_name=table2.column_name> WHERE<condition>; Example of INNER JOIN in SQL- SELECTOrders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName FROMOrders INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID; –Records in the Orders table that don’t have matches in…

HOW TO USE LEFT JOIN IN SQL?
LEFT JOIN/LEFT OUTER JOIN clause select all the records from left table(table1) and the matching records from the right table(table2). Syntax of LEFT JOIN in SQL- SELECT <column_name(s)> FROM <table1> LEFT JOIN<table2> ON <table1.column_name=table2.column_name> WHERE<condition>; Example of LEFT JOIN in SQL- SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID FROMCustomers LEFT JOIN Orders ONOrders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID; LEFT JOIN returns all records from the left table (Customers),…

HOW TO USE RIGHT JOIN IN SQL?
RIGHT JOIN/RIGHT OUTER JOIN clause select all the records from right table(table2) and the matching records from the left table(table1). Syntax of RIGHT JOIN in SQL- SELECT <column_name(s)> FROM <table1> RIGHT JOIN<table2> ON <table1.column_name=table2.column_name>WHERE<condition>; Example of RIGHT JOIN in SQL- SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID FROMCustomers RIGHT JOIN Orders ONOrders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID; RIGHT JOIN returns all records from the right table (Orders), even…

HOW TO USE FULL OUTER JOIN IN SQL?
FULL JOIN/FULL OUTER JOIN clause returns all the records when there is a match in left(table1) or right(table2) Syntax of FULL OUTER JOIN in SQL- SELECT <column_name(s)> FROM <table1> FULL OUTER JOIN<table2> ON <table1.column_name=table2.column_name> WHERE<condition>; Example of FULL OUTER JOIN in SQL- SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID FROMCustomers FULL OUTER JOIN Orders ONOrders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID; FULL OUTER JOIN returns all records from both…

HOW TO USE SELF JOIN IN SQL?
SELF JOIN is a regular join used to join the table with itself. Syntax of SELF JOIN in SQL- SELECT <column_name(s)> FROM <table1> t1, <table1>t2 WHERE<condition>; Example of SELF JOIN in SQL- SELECT A.CustomerName AS Customer1, B.CustomerName AS Customer2, A.CityFROM Customers A, Customers BWHERE A.CustomerID <> B.CustomerIDAND A.City = B. City; — SELF JOIN query customers that are from the same city.
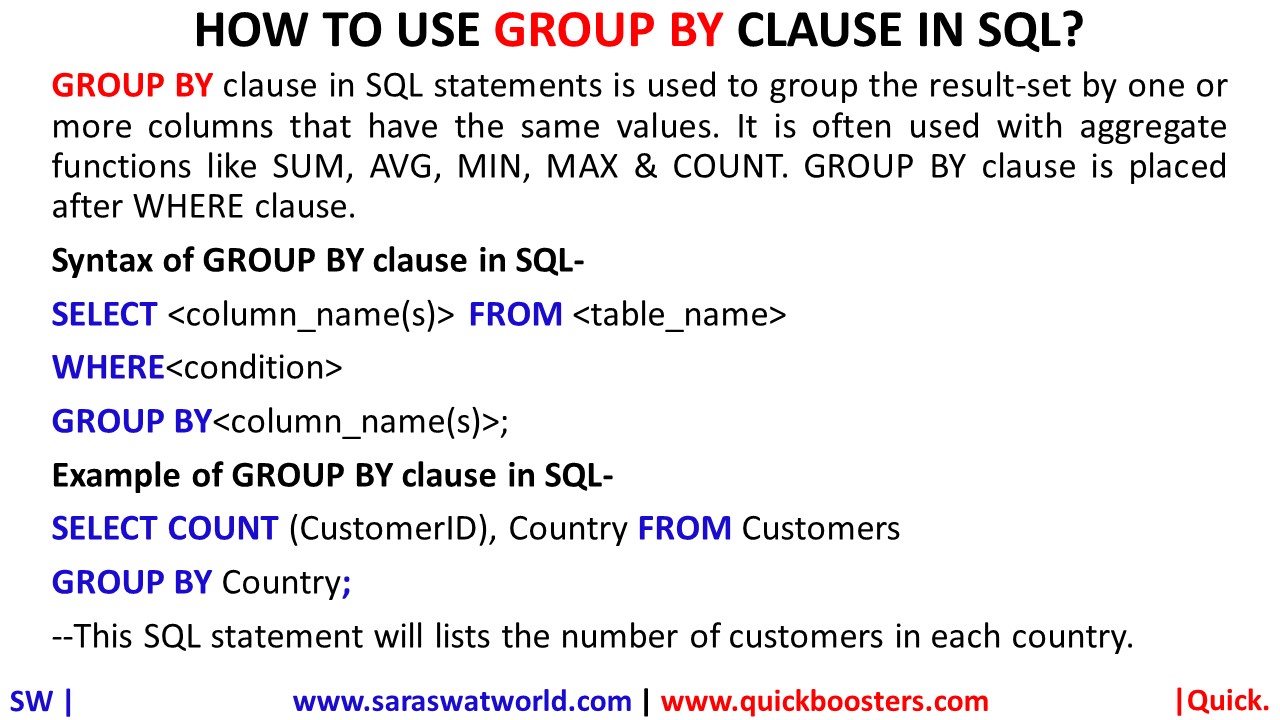
HOW TO USE GROUP BY CLAUSE IN SQL?
GROUP BY clause in SQL statements is used to group the result-set by one or more columns that have the same values. It is often used with aggregate functions like SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX & COUNT. GROUP BY clause is placed after WHERE clause. Syntax of GROUP BY clause in SQL- SELECT <column_name(s)> FROM <table_name> WHERE<condition> GROUP BY<column_name(s)>;…